This example shows a compact image-analysis pipeline that detects bright blobs in two sample images using DataJoint. It demonstrates:
Seeding a small
Imagemanual table with two entries of standard images fromskimage.data.Defining multiple parameter sets for blob detection in a lookup table
BlobParamSetDefining a computed master table
Detectiontogether with its nested part tableDetection.Blob.Populating the master, which automatically inserts all part rows inside the same transaction.
Visualizing the results by drawing detection circles on the images.
Visually selecting the optimal parameter set for each image and saving the selection in a manual table
SelectDetection.
Along the way we illustrate why master-part relationships are ideal for computational workflows: the master stores aggregate results and the parts hold per-feature detail, all created atomically.
Setup¶
Load the required images and display them for reference.
%xmode minimalException reporting mode: Minimal
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage import data
from skimage.feature import blob_doh
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
import datajoint as dj
schema = dj.Schema('image_analysis')@schema
class Image(dj.Manual):
definition = """
image_id : int
---
image_name : varchar(30)
image : longblob
"""
Image.insert(
(
(1, "hubble deep field", rgb2gray(data.hubble_deep_field())),
(2, "human mitosis", data.human_mitosis()/255.0)
), skip_duplicates=True
);fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 5))
for ax, image, title in zip(axs, *Image.fetch("image", "image_name")):
ax.imshow(image, cmap="gray_r")
ax.axis('off')
ax.axis('equal')
ax.set_title(title)

@schema
class BlobParamSet(dj.Lookup):
definition = """
blob_paramset : int
---
min_sigma : float
max_sigma : float
threshold : float
"""
contents = [
(1, 2.0, 6.0, 0.001),
(2, 3.0, 8.0, 0.002),
(3, 4.0, 20.0, 0.01),
]
@schema
class Detection(dj.Computed):
definition = """
-> Image
-> BlobParamSet
---
nblobs : int
"""
class Blob(dj.Part):
definition = """
-> master
blob_id : int
---
x : float
y : float
r : float
"""
def make(self, key):
# fetch inputs
img = (Image & key).fetch1("image")
params = (BlobParamSet & key).fetch1()
# compute results
blobs = blob_doh(
img,
min_sigma=params['min_sigma'],
max_sigma=params['max_sigma'],
threshold=params['threshold'])
# insert master and parts
self.insert1(dict(key, nblobs=len(blobs)))
self.Blob.insert(
(dict(key, blob_id=i, x=x, y=y, r=r)
for i, (x, y, r) in enumerate(blobs)))dj.Diagram(schema)Detection.populate(display_progress=True)Detection: 100%|██████████| 6/6 [00:01<00:00, 4.04it/s]
{'success_count': 6, 'error_list': []}Detection()Parameter sets¶
Define a small lookup table of blob-detection parameters.
fix, axes = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(10, 6))
for ax, key in zip(axes.ravel(), Detection.fetch("KEY", order_by="image_id, blob_paramset")):
img = (Image & key).fetch1("image")
ax.imshow(img, cmap="gray_r")
ax.axis('off')
ax.axis('equal')
ax.set_title(str(key), fontsize=10)
for x, y, r in zip(*(Detection.Blob & key).fetch("y", "x", "r")):
c = plt.Circle((x, y), r*1.2, color='r', alpha=0.5, fill=False)
ax.add_patch(c)
plt.suptitle("Detected blobs - all paramsets")
plt.tight_layout()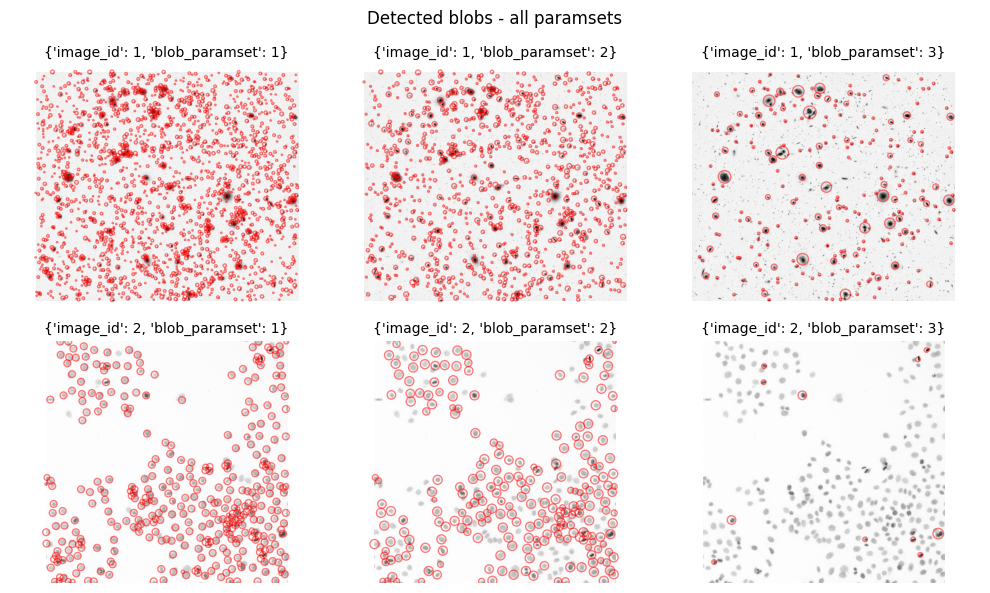
@schema
class SelectDetection(dj.Manual):
definition = """
-> Image
---
-> Detection
"""
SelectDetection.insert1(dict(image_id=1, blob_paramset=3))
SelectDetection.insert1(dict(image_id=2, blob_paramset=1))dj.Diagram(schema)fix, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8, 4))
for ax, key in zip(axes.ravel(), SelectDetection.fetch(as_dict=True, order_by="image_id")):
img = (Image & key).fetch1("image")
ax.imshow(img, cmap="gray_r")
ax.axis('off')
ax.axis('equal')
ax.set_title(str(key), fontsize=10)
for x, y, r in zip(*(Detection.Blob & key).fetch("y", "x", "r")):
c = plt.Circle((x, y), r*1.2, color='r', alpha=0.5, fill=False)
ax.add_patch(c)
plt.suptitle("Selected detections", fontsize=16)
plt.tight_layout()

Detection master and part tables¶
Detection is a computed table. When populate() runs, its make() method:
Fetches the image and parameter set.
Runs
skimage.feature.blob_dohto compute blobs.Inserts one master row with the blob count.
Inserts one
Detection.Blobpart row per blob (containing coordinates and radius).
If any insert fails, the transaction is rolled back so master and parts stay synchronized.
Results¶
Populate the detection table and display both the master summary and the per-blob annotations.
Takeaways¶
Master-part tables capture the structure “one job → many detailed results”.
Downstream analyses depend only on the master (
-> Detection) yet can access part details when needed.Populating the master guarantees atomic creation of all associated parts, preserving workflow integrity.
schema.drop() # drop the schema for re-generating the tutorial from scratch.